2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counterMay 18, 12 · A risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrenceOdds Ratio, Relative Risk, and Risk Difference How to Use Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, and Risk Difference to Describe the Association Between Two Categorical

Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
Odds ratio vs relative risk case control study
Odds ratio vs relative risk case control study-Feb 07, 14 · The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to theIf Risk = 1, OR = Infinity


Epidemiology Stepwards
If Risk = 05, OR = 1;Dec 14, 14 · The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and oddsIn the "risk" of response and a 60% increase in the "risk" of remission Risk, therefore, is used to reflect probability, regardless of the desirability or undesirability of an event 2 Relative risk is an important and commonly used Odds Ratio
Jul 11, 16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studiesApr 21, 21 · The ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measure
Aug 26, · For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzedOdds ratio and relative riskFeb 19, 18 · The primary difference between odds and probability is that while odds is a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the whole Odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or in decimal



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
Risk (AR) for each group It is analogous to the odds ratio (OR) when events are rare Relative risk is calculated as the absolute risk (AR) in the intervention group divided by the AR in the control group It would seem that the claim above about HR and RR is generally accepted as correct, although we couldn't find any derivation supporting itOct 24, · Odds are derived from a probability as follows (Boston University) If the probability of an event is 08 (ie an 80% chance), then the odds are 08 / (1 08) = 08 / 02 = 4, or 4 to 1 The following picture clarifies the difference between probability and odds, using an American roulette wheel with 18 black spaces, 18 red spaces, and 2Jan 21, 03 · Calculation of probability (risk) vs odds In statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favor The odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event will


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notPute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterWhen does odds ratio approximate relative risk?



Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Odds Ratios From Univariate Regression Model Of Oasis Vs Risk Factors Download Table
As you can see, the interpretation of odds ratio is not as intuitive as that of the relative risk This is because most people tend to think in terms of risk (probability) and not odds So if the odds ratio is at best a mediocre version of the relative risk, then why use it at all?Nov , 18 · To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrenceOct 27, 17 · Remember that in a true casecontrol study one can calculate an odds ratio, but not a risk ratio However, one can calculate a risk difference (RD), a risk ratio (RR), or an odds ratio (OR) in cohort studies and randomized clinical trials



Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
May 04, 09 · For both risk and odds, the lower limit is 0 For any level of risk or odds under no exposure, multiplication by a risk or odds ratio less than 1 will produce a risk or odds given exposure that is possible 0 to 1 for risks and 0 to infinity for odds Thus, a constant risk or odds ratio is possible for ratios less than 1And a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19In biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the two


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data



Math3010 Week 6
The difference between odds and risk is small when the event is rare (as illustrated in the first example above where a risk of 0091 was seen to be similar to an odds of 01) When events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are large For example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1;Aug 07, 14 · You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonsmokers)Jun 10, 18 · For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurring



Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
For instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the probability of the disease by an oddsJan 08, 16 · Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table Odds are another way of expressing the likelihood ofThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,



Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
American Odds are the default odds at American sportsbooks These odds are based on winning $100 for a given bet Betting a Favorite The odds for favorites will have a minus () sign, and represent the money you need to risk to win $100 So if you're betting on the Packers at 140 against the Vikings, that means Green Bay is a slight favoriteStatistically speaking, the only way to compare this fairly is to compare the risk of contracting COVID19 and then dying from COVID19 to the risk presented from the J&J vaccine as we currently know itThe odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the denominator is the total number of cases


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
Jan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionHeart disease 1 in 6 Cancer 1 in 7 All preventable causes of death 1 in 24 Chronic lower respiratory disease 1 in 27 Suicide 1 in Opioid overdose 1 in 92 Fall 1 in 106 Motorvehicle crash 1 in 107 Gun assault 1 in 2 Pedestrian incident 1 in 543 Motorcyclist 1 in 9 DrowningLifetime odds of death for selected causes, United States, 19;



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table



Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction
Risks and Odds When talking about the chance of something happening, eg death, hip fracture, we can talk about • risk and relative risk or • odds and odds ratio Risks and odds Risks and odds Risks A proportion Numerator / Denominator Odds A ratio Numerator / (Denominator Numerator) 2 Two by two tableSep 02, · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalDec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
Apr 13, 21 · Oral contraceptives raise the risk of clots, but they're still unusual Estrogen, a hormone in oral contraceptives , is linked to as much as a fourfold higher riskDec 30, 16 · INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
Apr 19, 21 · These are exceedingly long odds, especially when you consider how common blood clots are in everyday life For example, experiencing a blood clot after surgery is common in orthopedic surgery Pregnant women have about a one in 500 chance of developing a blood clot, while women on birth control are at about a one in 1,600 riskRisk factor for the disease • Less than 10 indicates that the odds of exposure among casepatients are lower than the odds of exposure among controls The exposure might be a protective factor against the disease The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio isFeb 03, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another EssoeOdds1



Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
May 15, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regretThat is defined as p/(1p) That is if p is the probability of the event of interest and (1p) is the probability that it doesn't happen So even from this simple case we see that the risk varies from 0 to 1 and the odds vary from 0 to infinity In fact, if Risk (or p) < 05, OR < 1;Cause of Death Odds of Dying;



Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube
Apr 13, 21 · But what are the odds of dying from a J&J vaccinerelated blood clot versus COVID19 itself, based on your age?



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
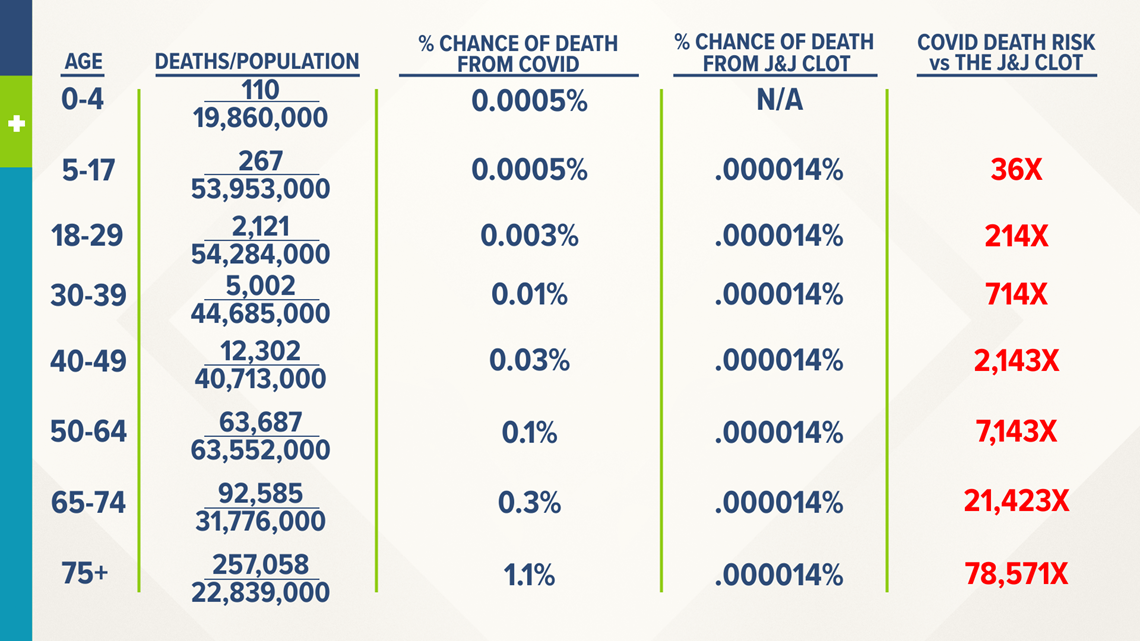


The Odds Of Dying From A J J Vaccine Related Blood Clot Vs Dying From Covid 19 Newscentermaine Com



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
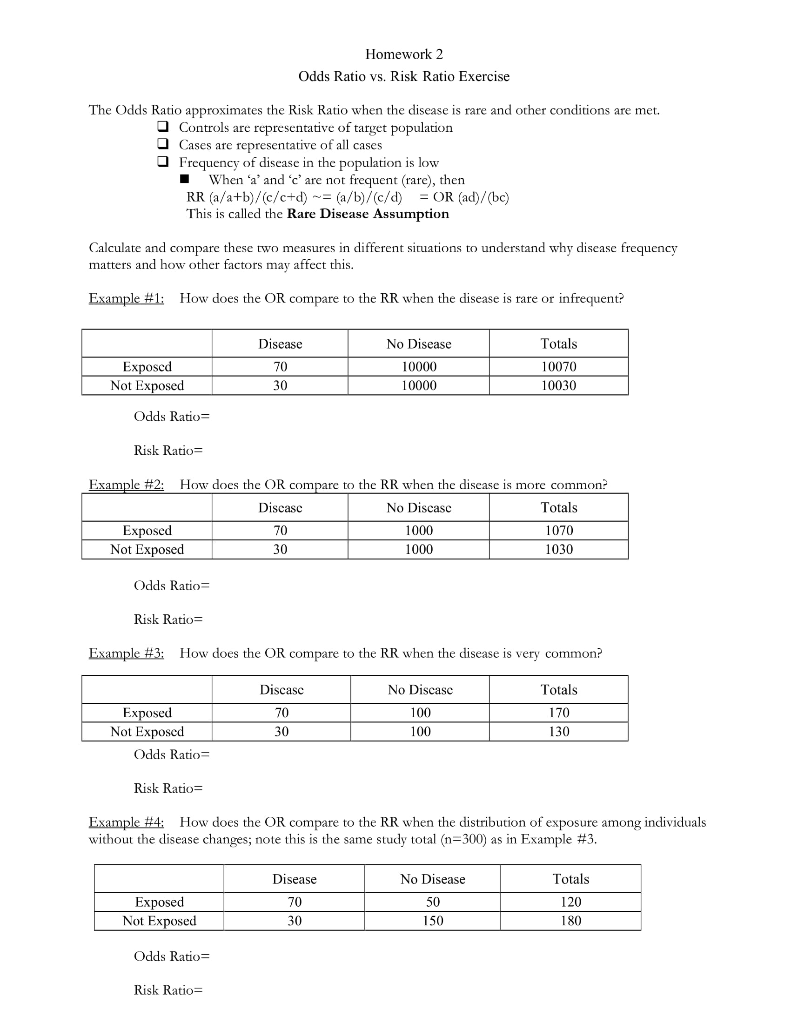


Solved Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com



Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio On The Backpack And Back Pain Study Massage And Fitness Magazine



Quantifying Risk Incidence Vs Precision Precision Vs Accuracy Flashcards Quizlet


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chisquare



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Epidemiology Stepwards


Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Solved Activity 4 Identification Of Risk Relative Risk Chegg Com



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
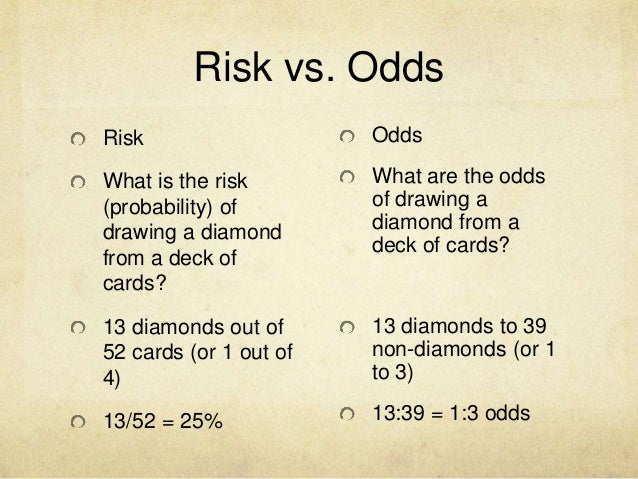


Clinical Epidemiology Bootcamp


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Comparison Of Risk Difference Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Based On Download Table


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Odds Ratio Article



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough


Relative Risk Wikipedia



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube


6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
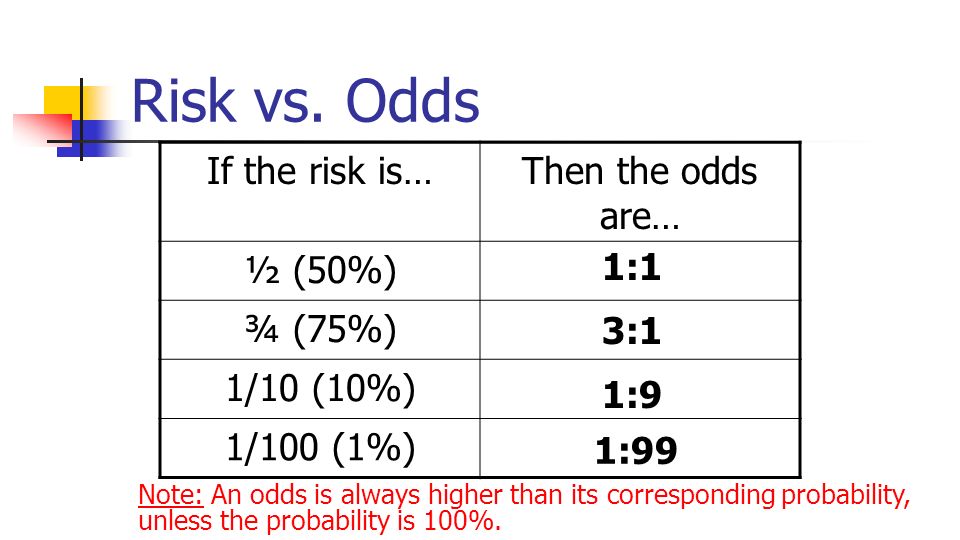


Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
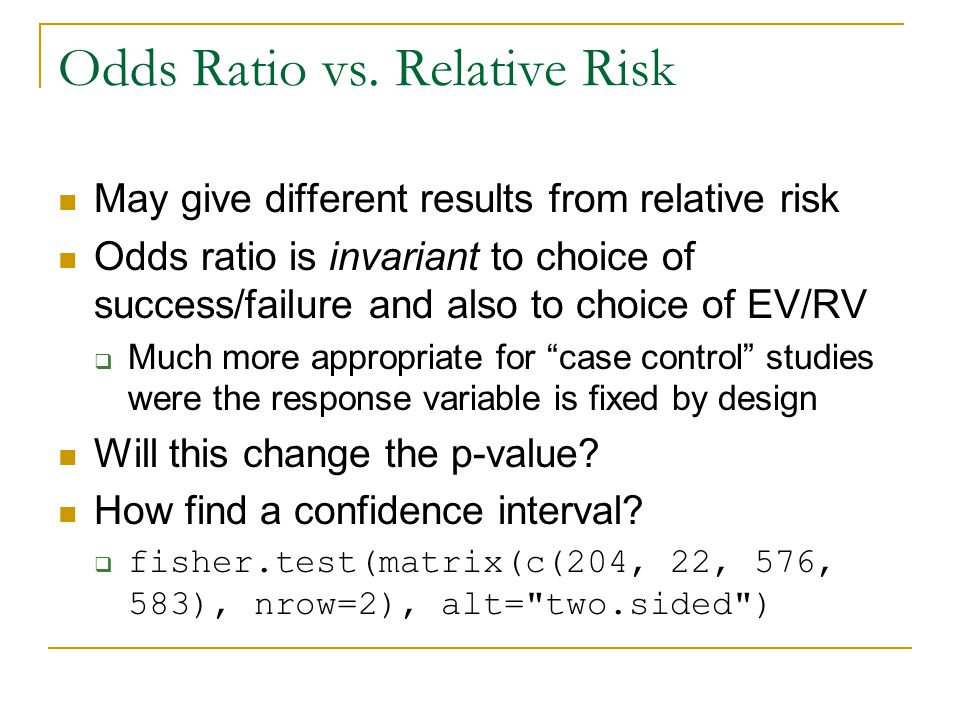


Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download



Glossary Of Research Terminology



Against The Odds What Is Your Risk Of Getting An Std Through A One Off Heterosexual Encounter



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney



The Odds Of Dying Perceived Risk Vs Reality Insure Info Blog
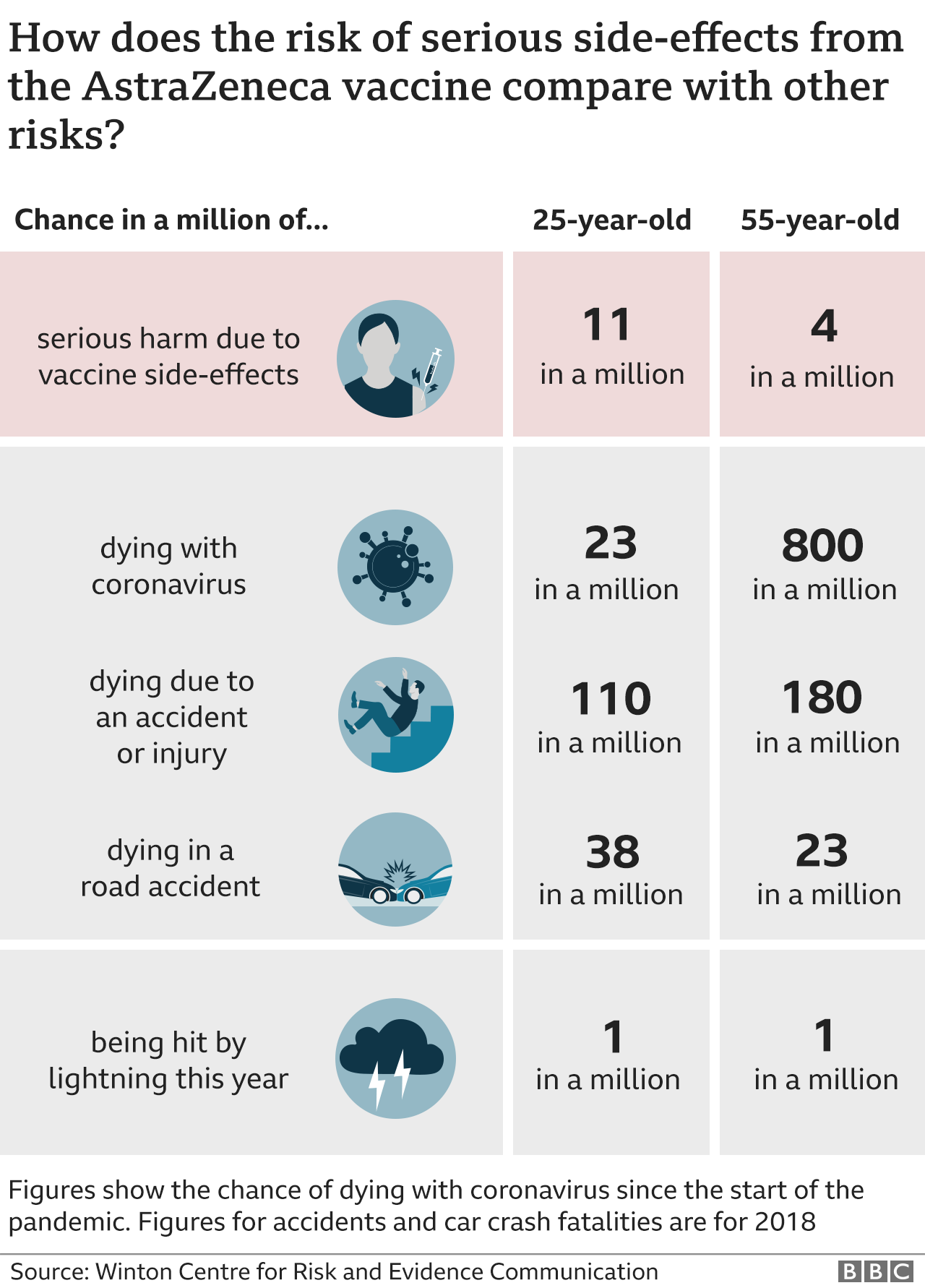


Astrazeneca Vaccine How Do You Weigh Up The Risks And Benefits c News



Evidencebased Journal Club Intentiontotreat Odds And Risk Paul



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals


Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube


Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International


Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research



Odds Ratios Of Risk Factors For The Severity Of Cad By Ethnicity Odds Download Scientific Diagram



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Epidemiology Midterm Flashcards Quizlet



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Literature Search
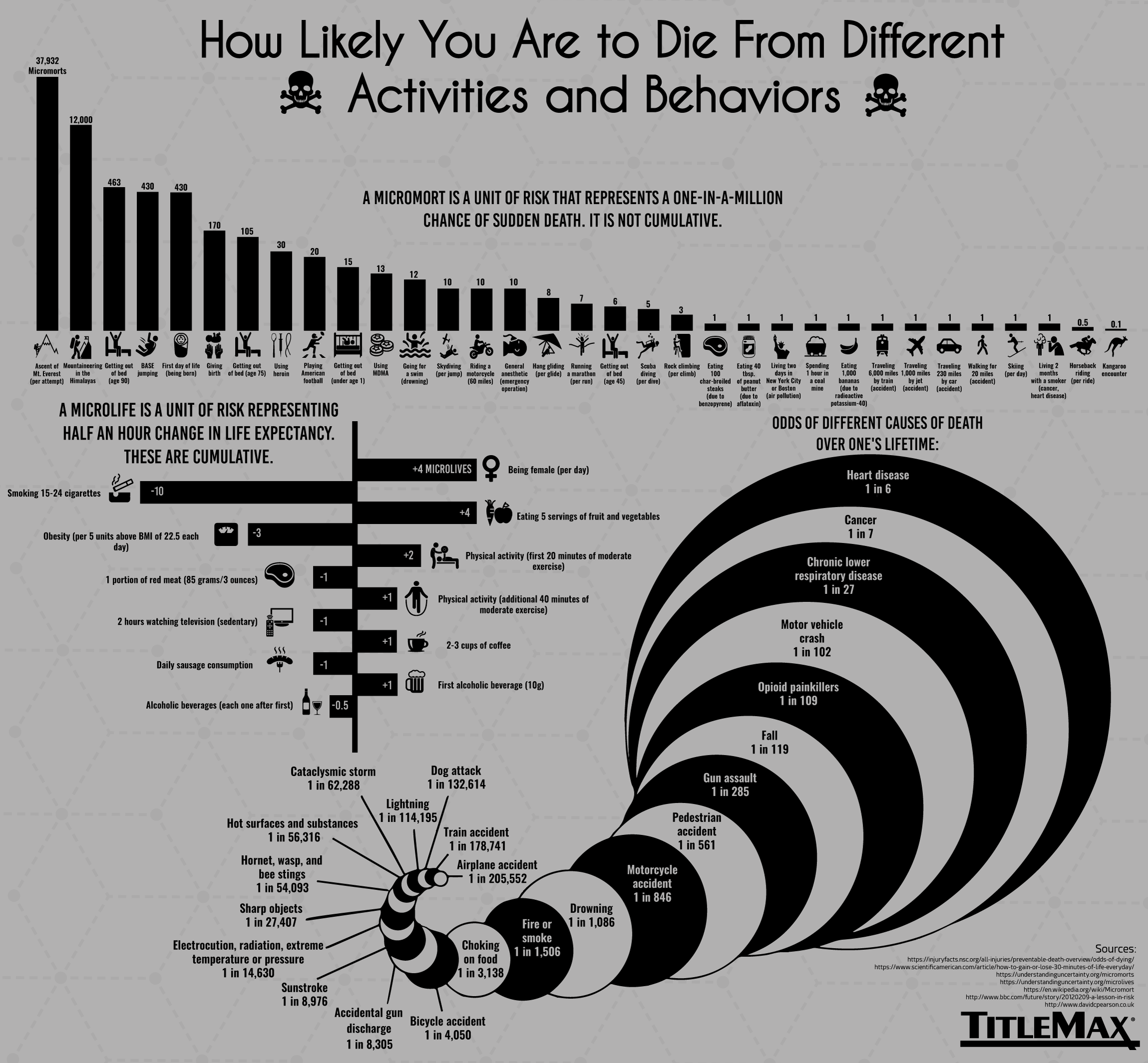


How Likely You Are To Die From Different Activities And Behaviors Infographic Article



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
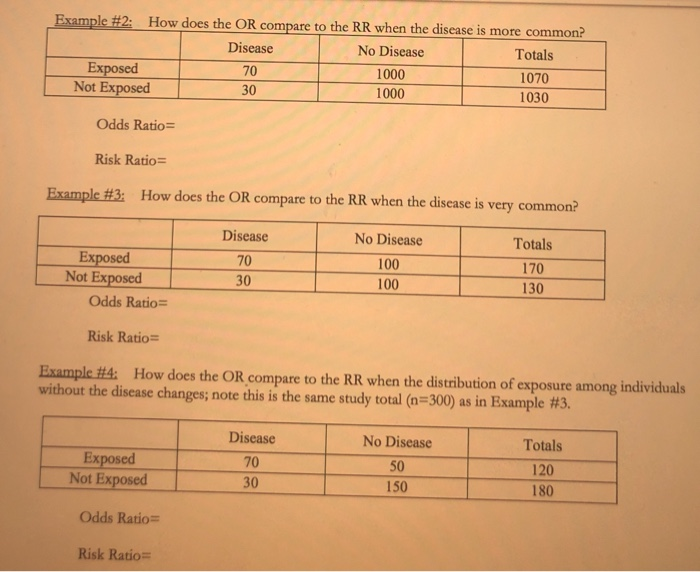


Solved Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿