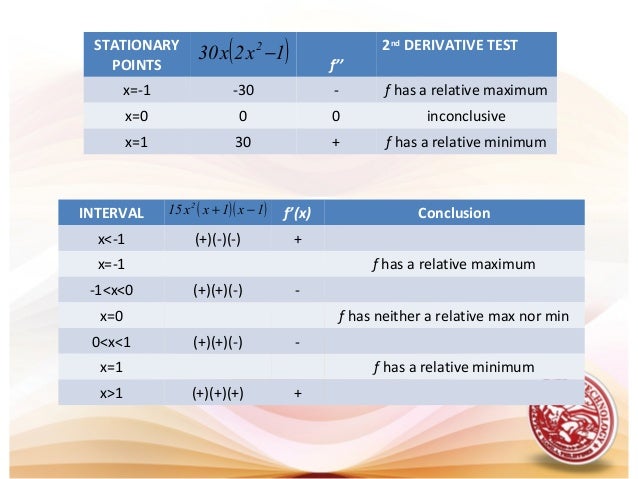
Thus, at the transition (from left to right) through the point \(x = 1\), the function changes from increasing to decreasing, ie \(x = 1\) is the maximum point of the function Similarly, \(x = 3\) is the minimum point of the function Figure 24 Figure 25 The equation is f(x) = (x) / (x^2 1) The Attempt at a Solution Well I first took the derivative, which was f'(x) = (x^2 1) / (x^2 1) ^2 I set it equal to zero to find the relative extremas, and I got X^2 1 = 0, which means X^2 = 1 That isn't a real number, but so would that mean there are no intervals where it's increasing or decreasing?Fyrir 2 dögum 0 Let f ( x) = ( 1 1 x) x and g ( x) = ( 1 1 x) x 1, both f and g being defined for x > 0, then comment about the increasing/decreasing nature of f ( x) and g ( x) f ( x) = e x ln ( 1 1 x) f ′ ( x) = ( 1 1 x) x ( x 1 1 x ⋅ − 1 x 2 ln
How To Find The Intervals In Which F X X 3 3x 2 Is Increasing In Which Interval Is It Decreasing Quora
How to tell if f(x) is increasing or decreasing
How to tell if f(x) is increasing or decreasing-At x = 1 2 the derivative is 3 Since this is negative, the function is decreasing on ( 1, 0) Decreasing on ( 1, 0) since f ′ ( x) < 0 Decreasing on ( 1, 0) since f′ (x) < 0 Substitute a value from the interval (0, 1) into the derivative to determine if the function is increasing or decreasingIf we are looking just for X
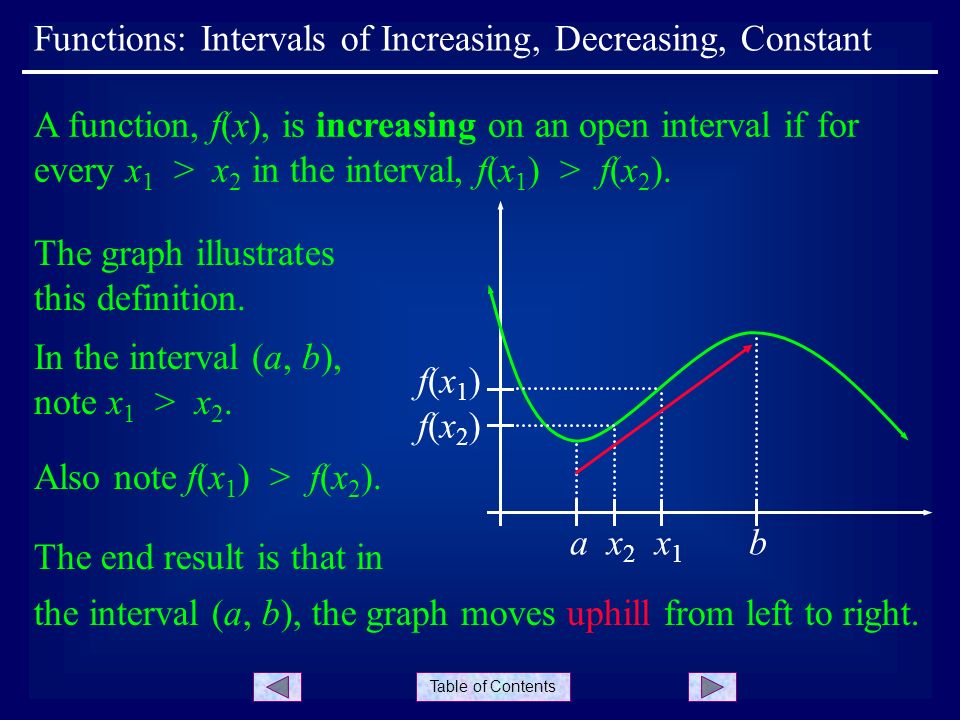



Table Of Contents Functions Intervals Of Increasing Decreasing Constant A Function F X Is Increasing On An Open Interval If For Every X 1 X 2 In Ppt Download
Figure 335 Number line for f in Example 332 In summary, f is increasing on the set ( − ∞, − 1) ∪ (3, ∞) and is decreasing on the set ( − 1, 1) ∪ (1, 3) Since at x = − 1, the sign of f'\ switched from positive to negative, Theorem 332 states that f( − 1) is a relative maximum of fSolutionShow Solution f (x) `= "x" 1/"x", "x" in "R"` `therefore "f"' ("x") = 1 ( 1/"x"^2) = 1 1/"x"^2` `∵ "x" ne 0,` for all values of x, `"x"^2>0` `therefore 1/"x"^2 > 0, 1 1/"x"^2` is always positive thus f' (x)>o , for all x ∈ RAdvertisement Remove all ads Advertisement Remove all ads Sum Show that f (x) = e 1/x , x ≠ 0 is a decreasing function for all x ≠ 0 ?
A function can be decreasing at a specific point, for part of the function, or for the entire domain A monotonically decreasing function is always headed down;You can find other Test Increasing And Decreasing Functions extra questions, long questions & short questions for JEE on EduRev as well by searching above QUESTION 1 Separate the interval into subintervals in which f (x) = sin4 x cos4 x is increasing or decreasingLastly, g0(5) = 1 64 (5)3 = 1 64 125 > 0 So g0(x) will be positive everywhere in (4;1), and thus g is increasing on (4;1) 92 Extrema and the First Derivative Test We now have enough information to sketch these graphs 1 First let's graph f(x) = x3 4
Help your child succeed in math at https//wwwpatreoncom/tucsonmathdocfind the intervals on which the given function is increasing and the intervals on whi41 Increasing and Decreasing Functions ©10 Iulia & Teodoru Gugoiu Page 1 of 2 41 Increasing and Decreasing Functions A Increasing and Decreasing Functions A function f is increasing over the interval (a,b)if f (x1)< f (x2)whenever x1Since this is negative, the function is decreasing on ( − ∞, − 1 2) Decreasing on ( − ∞, − 1 2) since f ' ( x) < 0 Decreasing on (−∞,−1 2) since f '(x) < 0 Substitute a value from the interval (−05,0) into the derivative to determine if the function is increasing or decreasing




The Graph Of The Function F X X 4 X 1 Is Shown Below Which Statement About The Function Is Brainly Com



Www Pnw Edu Wp Content Uploads 03 Lecture Notes 10 1 2 Pdf
Math Calculus Increasing And Decreasing Function 503 150 The function f (x) = 1 ∣x∣x is (a) strictly increasing (b) strictly decreasing (c) neither increasing nor decreasingIncreasing/Decreasing Test If f′(x) > 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is increasing on (a,b) If f′(x) < 0 for all x ∈(a,b), then f is decreasing on (a,b) First derivative test Suppose c is a critical number of a continuous function f, then Defn f is concave down if the graph of f lies below the tangent lines to f Misc 7 Find the intervals in which the function f given by f (x) = x3 1/𝑥^3 , 𝑥 ≠ 0 is (i) increasing (ii) decreasing f(𝑥) = 𝑥3 1/𝑥3 Finding f'(𝒙) f'(𝑥) = 𝑑/𝑑𝑥 (𝑥^3𝑥^(−3) )^




Intervals In Which Function Is Increasing Or Decreasing Problem Example 1 Youtube



Solved Find The Intervals Of Increasing Decreasing For The Function F X X 3e X Course Hero
The function f(x) = x 1/x is (A) Increasing in (1, ∞) (B) Decreasing in (1, ∞) Increasing in (1, ∞), decreasing in (e, ∞) (D) Decreasing in (1, e), increasing in (e, ∞)This video screencast was created with Doceri on an iPad Doceri is free in the iTunes app store Learn more at http//wwwdocericomIf f(x) is strictly increasing it's slope (derivative must be positive d f(x)/dx = 4 x^3 4 4 x^ 3 4 =0 X ^3 =1 X = 1 If x > 1 then slope is positive So f(x) is strictly increasing in the domain ( 1 , infinity ) and in the range ( 3 , infinity)



Q Tbn And9gcr1awjnfievvbxtiltp6vsfzl Yvhcce0yraat7t Hr3 P37lem Usqp Cau



Http Media Collegeboard Com Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q5 Pdf
Find the intervals in which f (x) is increasing or decreasing (i) f (x) = x ∣ x ∣, x ∈ R (ii) f (x) = sin x ∣ sin x ∣, 0 < x ≤ 2 π (iii) f (x) = sin x (1 cos x), 0 < x < 2 πFunctions are increasing, decreasing and constant when you plot the graph of the function in a coordinate system Let's define the meaning of these functions Increasing function A function is increasing in an interval for any and if implies Example Let be a function Find all the values for the function to plot the graph x Explanation to determine if a function f (x) is increasing/decreasing at x = a evaluate f '(a) ∙ if f '(a) > 0 then f (x) is increasing at x = a ∙ if f '(a) < 0 then f (x) is decreasing at x = a differentiate f (x) using the quotient rule given f (x) = g(x) h(x) then



Http Sites Lafayette Edu Thompsmc Files 15 08 Section 3 3 Pdf




Table Of Contents Functions Intervals Of Increasing Decreasing Constant A Function F X Is Increasing On An Open Interval If For Every X 1 X 2 In Ppt Download
Procedure to find where the function is increasing or decreasing Find the first derivative Then set f' (x) = 0 Put solutions on the number line Separate the intervals Choose random value from the interval and check them in the first derivative If f (x) > 0, then the function is increasing in that particular intervalAs x increases in the positive direction, f(x) always decreases The point where a graph changes direction from increasing to decreasing (or decreasing to increasing) is called a turning point or inflection pointThe total cost C(x) in Rupees associated with the production of x units of an item is given by C(x) = 0007 x – 0003 x 2 15 x 4000 Find the marginal cost when 17 units are produced Here



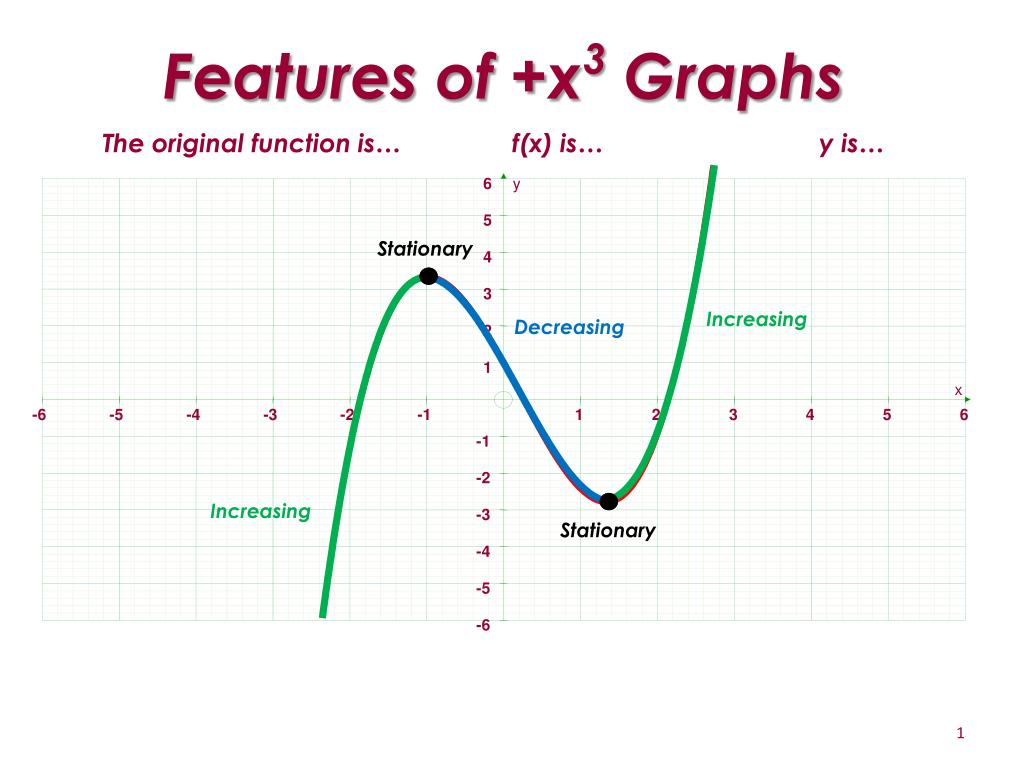
1
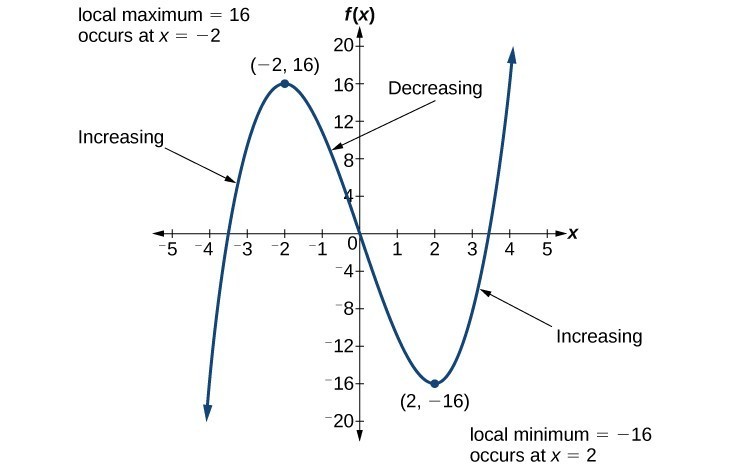



Use A Graph To Determine Where A Function Is Increasing Decreasing Or Constant College Algebra
Given f '(x) = (2 x)(6 x), determine the intervals on which f(x) is increasing or decreasing Math 1 determine the interval(s) where the function f(x)= 1 / 2x10 is a) positive b) Increasing 2 Consider the function f(x) = 3 / 4x5 a) Determine the key features of the function i) Domain and range ii)Intercepts iii) Equations Get an answer for '`f(x) = x/(x^2 1)` (a) Find the intervals on which `f` is increasing or decreasing (b) Find the local maximum and minimum values of `fIf the signal inverted from "" it means f(x) for this interval is a decreasing function, because only decreasing functions are able to invert inequalities CONCLUSION If we are looking just for X>0 the function f(x) = 1/x is a decreasing function;




Show That F X X 1 X Is Increasing For All X In R Where X 0



Find The Intervals Of Increasing And Or Decreasing Chegg Com
Advertisement Remove all adsMath Calculus Increasing And Decreasing Function 502 150 Function f (x) = ∣x∣ − ∣x − 1∣ is monotonically increasing when (a) x < 0 (b) x > 1 (c) x < 1 (d) 0 < x < 1 502 150 1169 k 9 k Answer Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring excellent marks in exams Image Solution Find answer in image to clear your doubt instantly Determine the values of for which is increasing or decreasing 28k



Q Tbn And9gcqfhuxhmizntsns V1x7khz5m A5m8vqbqk2v3lmpebzl 5tjrm Usqp Cau



Math Scene Functions 2 Lesson 2
If f(x)=x^34x^2lambdax1 is a monotonically decreasing function of x in the largest possible interval (2,2/3)dot Then (a ) lambda=4 (b) lambda=2 (c) lambda=1 (d) lambda has no real valueThe function f (x) = cos x 2px is monotonically decreasing for The function f (x) = log (1 x) (2x / 2 x) is increasing for all values of x, then The function f (x) = tan –1 (sinx cos x), x > 0 is always an increasing function on the interval For each of the following, determine if the function is increasing, decreasing, even, odd, and/or invertible on its natural domain $$f(x) = \frac{x}{x^21}$$



Increasing Decreasing Functions Examples



Increasing Decreasing Functions Examples
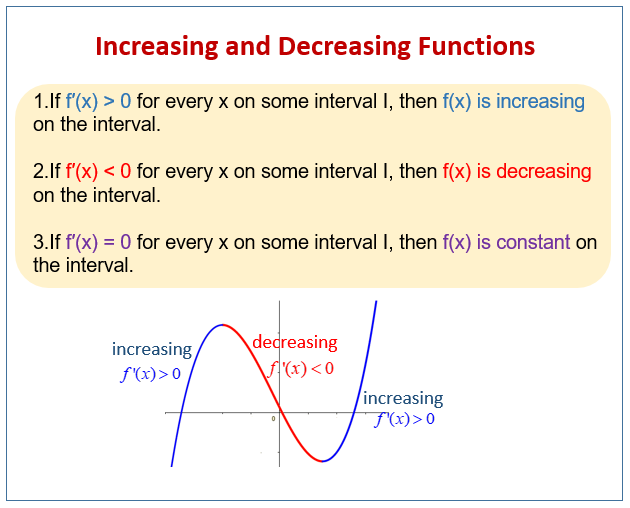
1) If f0(x) > 0 for all x in I, then f is increasing(%) on I 2) If f0(x) < 0 for all x in I, then f is decreasing(&) on I Proof We have proved the flrst result as a corollary of Mean Value Theorem in class Here to remind ourselves MVT we will prove the second one Let f0(x) < 0 on the interval I Pick any two points x1 and x2 in I where x1And now notice h ′ (x) = − 1 / x ⋅ (x 1)2 is negative, so h(x) is decreasing and minimal value is at ∞, but h( ∞) = 0 So, h(x) ≥ 0 f(t) = 1 tlog(1 t) is decreasing for t > 0, because it is smooth and its derivative is negative Its derivative is f ′ (t) = − 1 t2g(t), where g(t) = log(1 t) − t 1 tF (x) = 2 − x − x3 Show that f (x) is decreasing for all values of x (4 marks) show more Show that there isn't a turning point ie differentiate and equate to zero There shouldn't be a limit Then say something like the coefficients of the x terms are negative which shows it's decreasing 0



Day15




Determine Intervals In Which Following Functions Are Strictly Increasing Or Strictly Decreasing F R R F X X 1 X 2 2
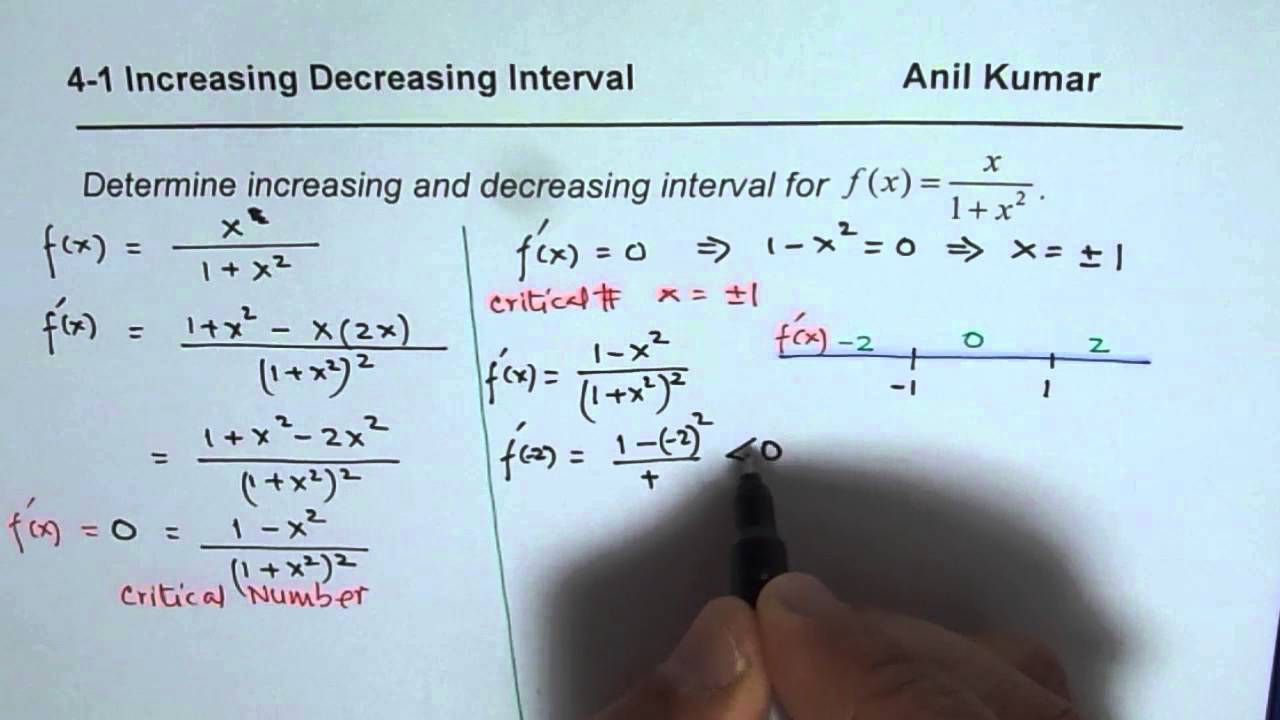
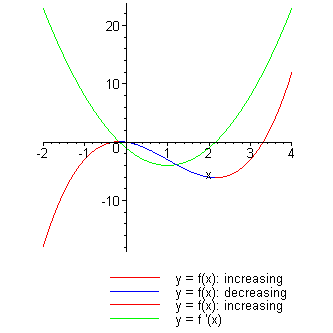
Where f(x) can change from increasing to decreasing etc These boundaries, x c, occur where f0(x) = 0 or f0(x) is unde ned these boundaries are the only places where f(x) can change from inc to dec or dec to inc 2nddetermine the sign of f0(x) at one test value of x between each boundary if f0(x) = () at this test value then it is increasingSolution Verified by Toppr Let us consider the problem (x1) 3(x−3) 3 Therefore, there are three region to check for function's increasing or decreasing nature (−∞,−1),(−1,3),(3,∞) (−∞,−1)→ By substitute any value less than (−1) greater than (3) (→) increasing (3,∞)→ we can say that function is positive → Increasing The function f is defined by f(x) = (x 2)e^–x is (a) decreasing for all x (b) decreasing in (– ∞, – 1) and increasing in (– 1, ∞)




View Question Properties Of This Reciprocal Function F X X 1 X 1




Consider The Function F X X Lnx Find The Intervals On Which F X Is Increasing And The Intervals Where It Is Decreasing Also Determine Any Relative Max Or Min Study Com
`f(x) = x^4 2x^2 3` (a) Find the intervals on which `f` is increasing or decreasing (b) Find the local maximum and minimum values of `f` (c) Find the intervals of concavity and the ∴ f'(x) > 0 f(x) is increasing on (0, 1) Since 0 < x < 157 099 < x99 < (157)99 0 × 100 < 100x99 < (157)99 × 100 0 < 100x99 < (157)99 × 100 Since 0 < x < 𝜋/2 So x is in 1st quadrant ∴ cos x is positive Thus, f(x) is strictly decreasing for none of the intervals So, (D) is the correct answer Show More



Www Beachwoodschools Org Downloads Ab 3 42 Pdf




Given F X 1 X 4 X Determine The Intervals On Which F X Is Increasing Or Decreasing Brainly Com




Help Needed With Calculus Question Wyzant Ask An Expert




Solve This Q Find The Intervals In Which The Function F X 3 Log 1 X Maths Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com



3
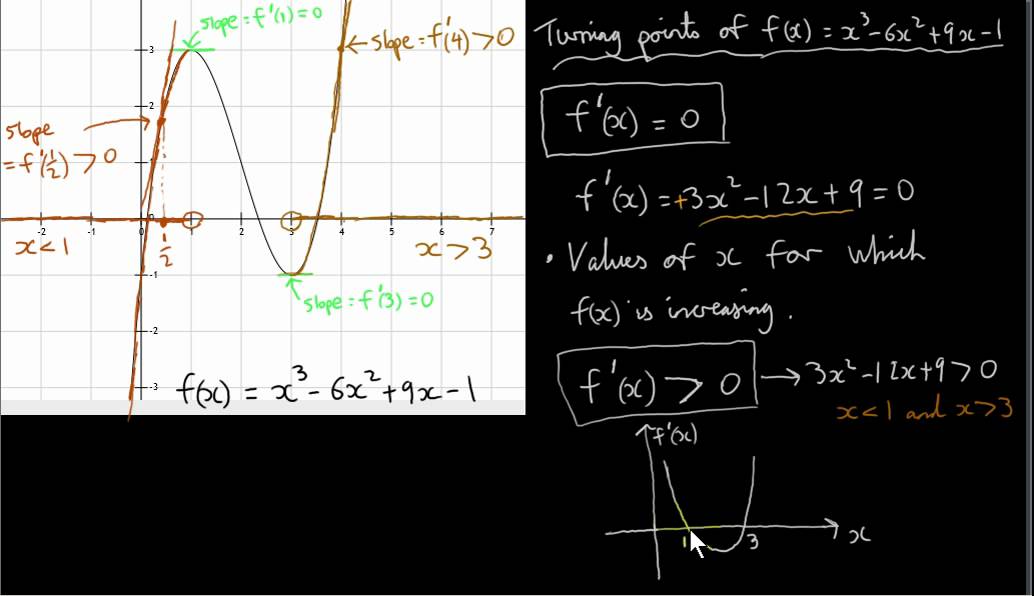



How To Find The Values Of X For Increasing And Decreasing F X Youtube



Finding The Values Of X When F X Is Increasing Decreasing The Student Room



Http Mysite Science Uottawa Ca Phofstra Mat1300 Lecture09 Pdf




Is The Function F X Increasing Or Decreasing Over The Interval 2 Lt X Lt 1 Brainly Com




Answered 1 For The Function F X X 1 E A Bartleby




Example 11 Find Intervals In Which F X Is Strictly Examples
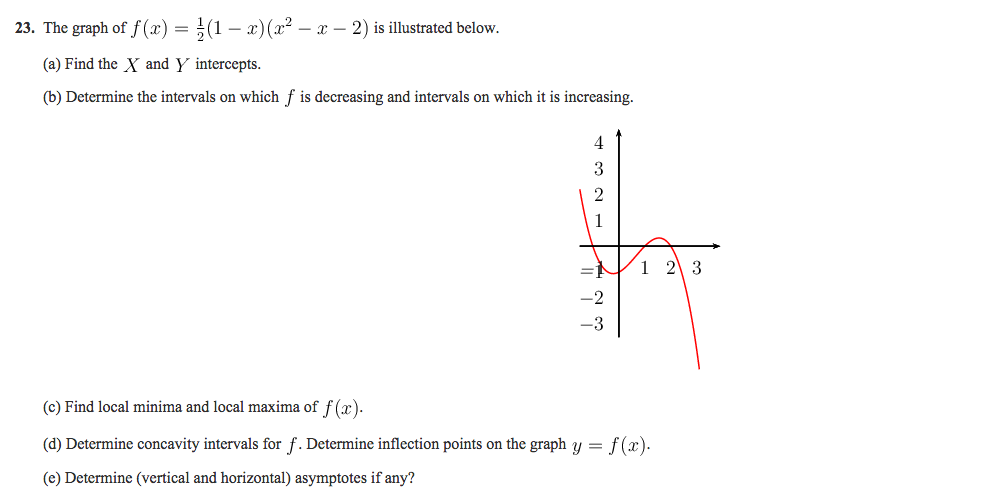



23 The Graph Of F X 1 2 1 X X 2 X 2 Is Chegg Com



Increasing And Decreasing Functions Page 2



Monotonically Increasing And Decreasing Functions An Algebraic Approach Opencurriculum



How To Find The Intervals In Which F X X 3 3x 2 Is Increasing In Which Interval Is It Decreasing Quora




Increasing And Decreasing Function 1 Strictly Increasing Function



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube



Solution Find Intervals On Which The Given Function Is Increasing And The Intervals On Which It Is Decreasing F X X 2 1 I 39 Ve Tried To Solve This And I 39 Ve Looked For Examples
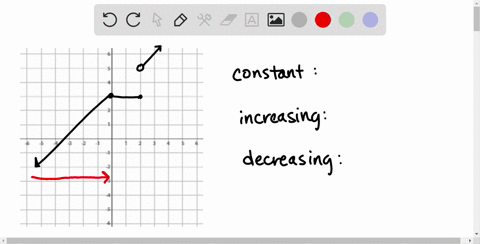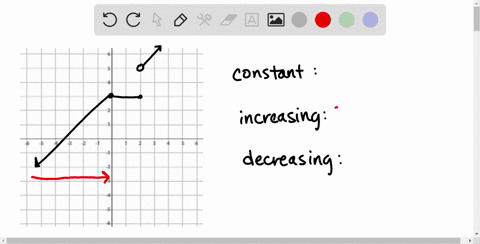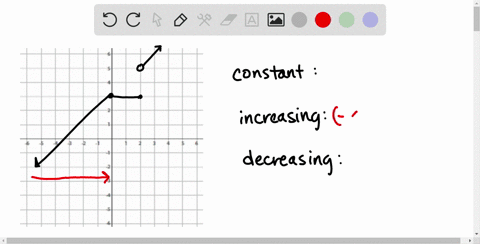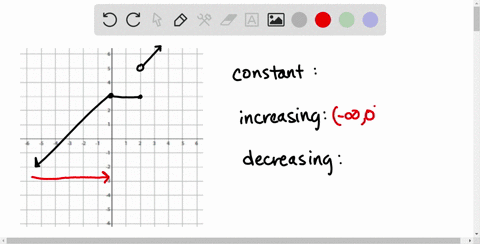



Solved In Exercises 39 46 Determine The Intervals Over Which The Function Is Increasing Decreasing Or Constant F X
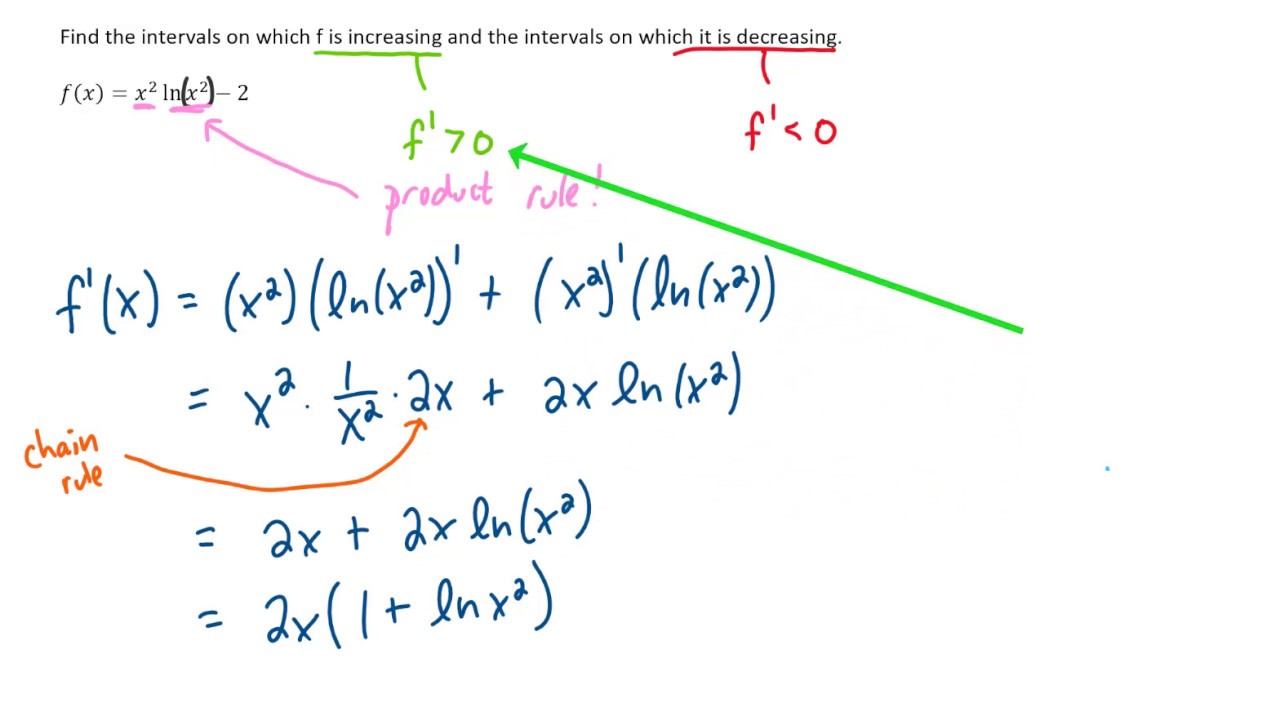



Calc 1 Pod 43 Find The Intervals On Which F Is Increasing And Decreasing F X X 2 Ln X 2 2 Youtube



Find The Intervals In Which The Following Functions Are Strictly Increasing Or Decreasing A 2x 3 9x 2 12x 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Determine The Intervals On Which The Function Fe 5x X 12 2x Homeworklib




Finding Decreasing Interval Given The Function Video Khan Academy




Prove That The Function F Given By F X X2 X 1 Is Neither Strictly Increasing Nor Strictly Decreasing On 1 1 Mathematics Shaalaa Com



Www Math Tamu Edu Mayaj Chapter5 Sec5p1completed Pdf
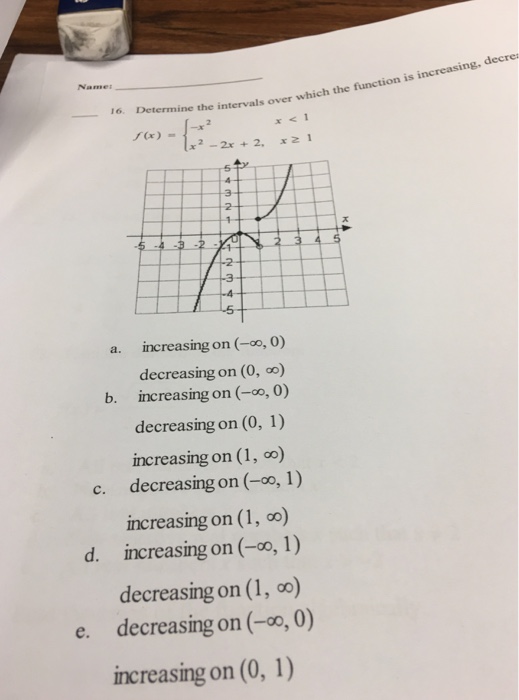



Determine The Intervals Over Which The Function Is Chegg Com




Let F X E X 1 X 1 X N N Where N In N Show That F Is Non Increasing On 0 Infinity Study Com



Determine The Intervals On Which The Function F X X Lnx Restricted To Positive X Is Increasing And Intervals On Which The Function Is Decreasing Enotes Com



I Seriously Don T Understand Increasing Decreasing Functions The Student Room



Find The Intervals In Which The Function F X X 1 3 X 2 2 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



Solution Given F X X X 2 9 Graph F Is The Function Increasing Or Decreasing In The Interval 3 Lt X Lt 3 G As X Approaches 3 From The Left What Happens To



Http Www Mast Queensu Ca Math121 Assignments Unit06 Pdf




Graphs Of Functions Text Example Solutionthe Graph Of F X X Is By Definition The Graph Of Y X We Begin By Setting Up A Partial Table Ppt Download



Http Smacmathapcalculus Weebly Com Uploads 1 9 2 5 Apc Hw Test 5 Extra Practice Key V2 Pdf




F R Gt R F X X 1 X 2 Determine Intervals In Which The Given Function Are Strictly Increasing Or Brainly In
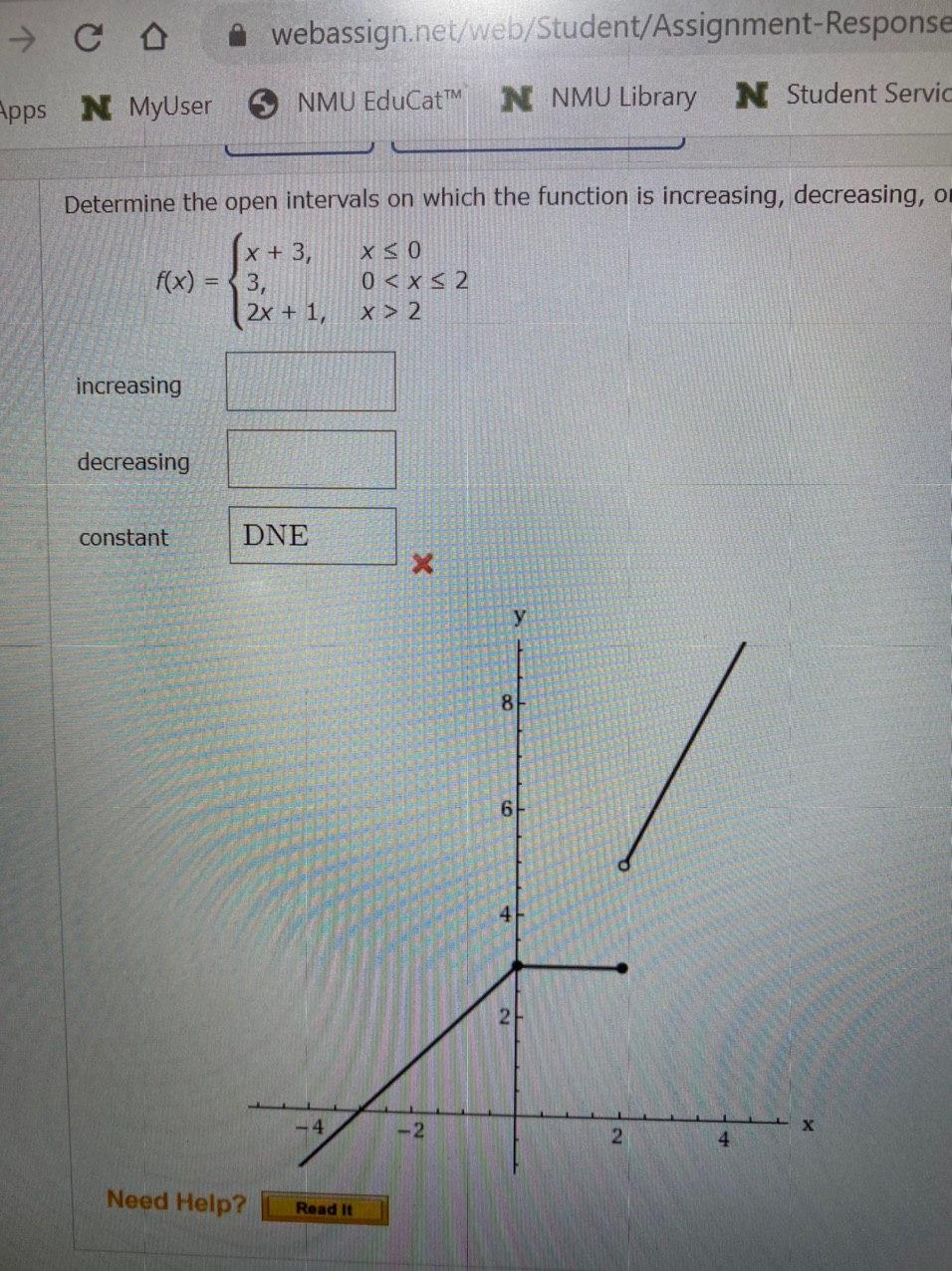



Answered Determine The Open Intervals On Which Bartleby



Increasing And Decreasing Functions
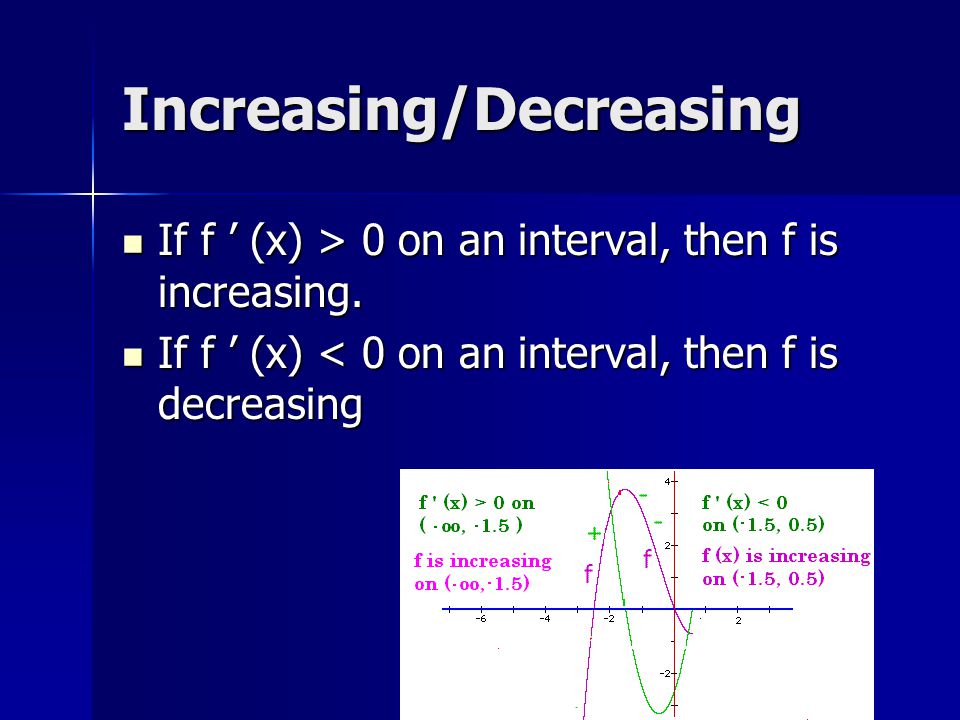



Increasing Decreasing Ppt Video Online Download
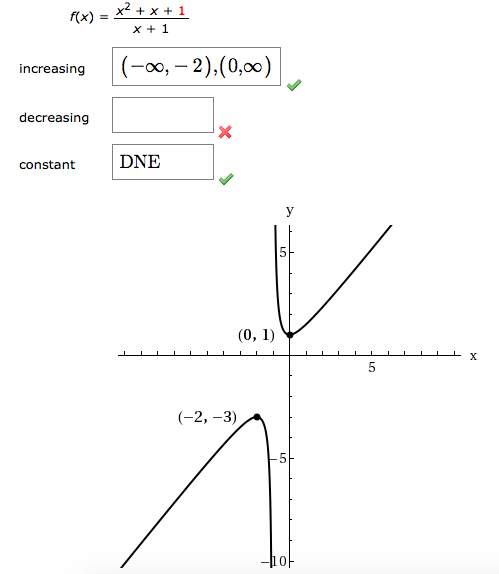



Determine The Intervals On Which The Function Is Chegg Com



Solved 1 Increasing And Decreasing Functions A Increasing And Decreasing Functions Ex 1 Find The Intervals Where The Function Y F X Is Increasi Course Hero



Www Hoodriver K12 Or Us Cms Lib Or Centricity Domain 230 Ch 5 pt answer key Pdf




Let I Be Any Interval Disjoint From 1 1 Prove That The Function F Given By F X X 1 X Is Strictly Increasing On I Mathematics Shaalaa Com



Ppt Increasing Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
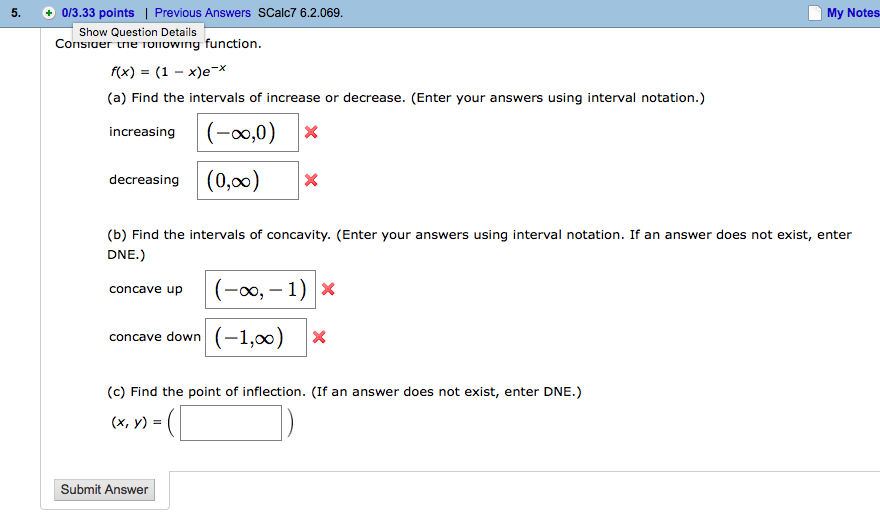



Consider The Following Function F X 1 X E X Chegg Com




Show That F X 1 X Is A Decreasing Function On 0 Oo




Six Basic Inverse Trigonometric Functions What Is Six Basic Inverse Trigonometric Functions Examples Solutions Cuemath




Classxii Sub Mathematics Topic Increasing Decreasing Increasing Decreasing




Increasing And Decreasing Functions



How To Find Increasing And Decreasing Interval For Continuous Rational Function Youtube



Increasing And Decreasing Functions Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos Activities



L19 Increasing Amp Decreasing Functions




Statement 1 The Function F X Ln X Is Increasing In 0 10 And G X 1 X Is Decreasing In 0 10 Statement 2 If A Differentiable Function Increases In The Interval A B Then



Localanalysis Html




Find The Intervals In Which F X Log 1 X X 1 X Is Increasing Or Decreasing Maths Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com
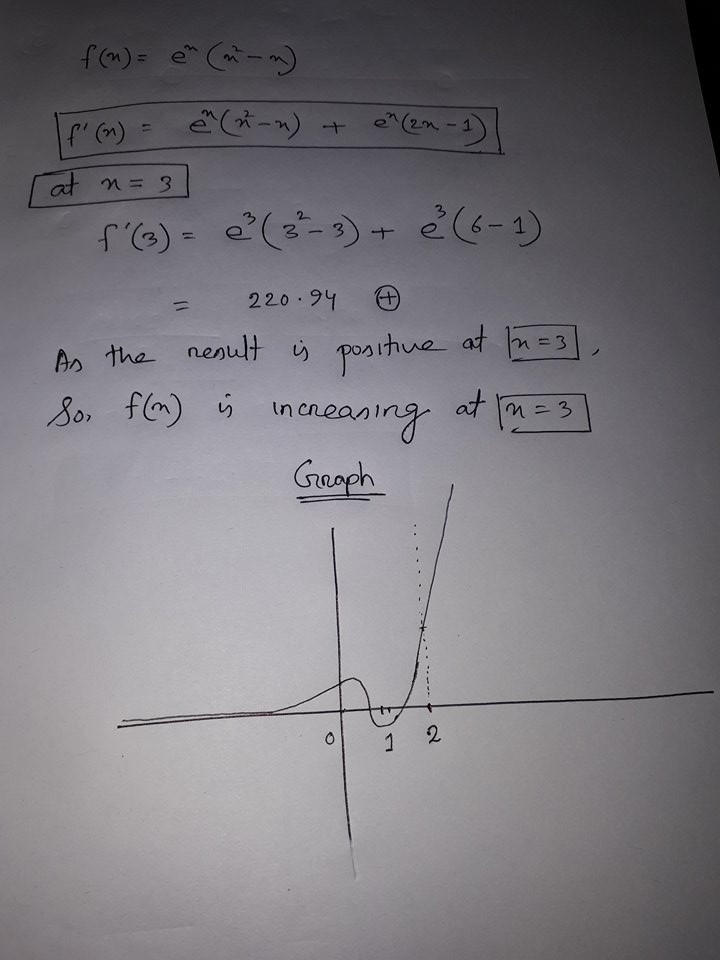



Is F X E X X 2 X Increasing Or Decreasing At X 3 Socratic



If F X X 4 8x 2 16 Then For Which Intervals Is F X Increasing Quora




2 1 Linear Functions Mathematics Libretexts




Determine The Values Of X For Which F X X 2 X 1 X 1 Is Increasing Or Decreasing
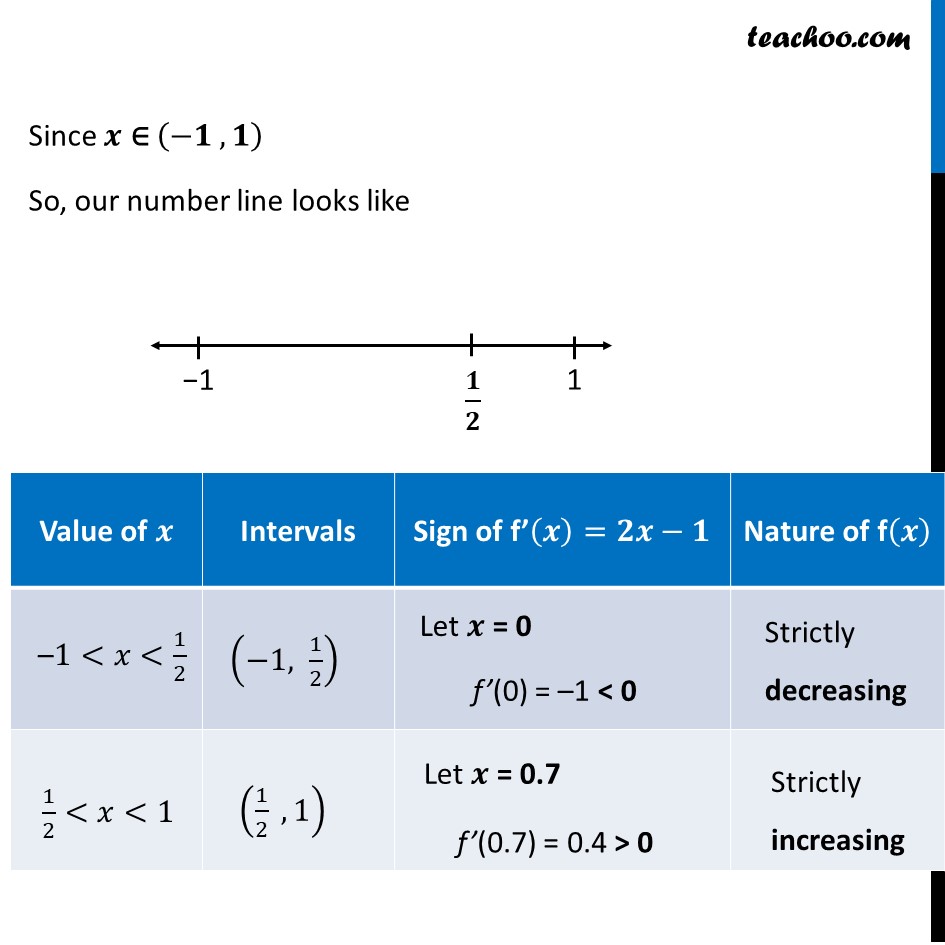



Ex 6 2 11 Prove F X X2 X 1 Is Neither Strictly Increasing
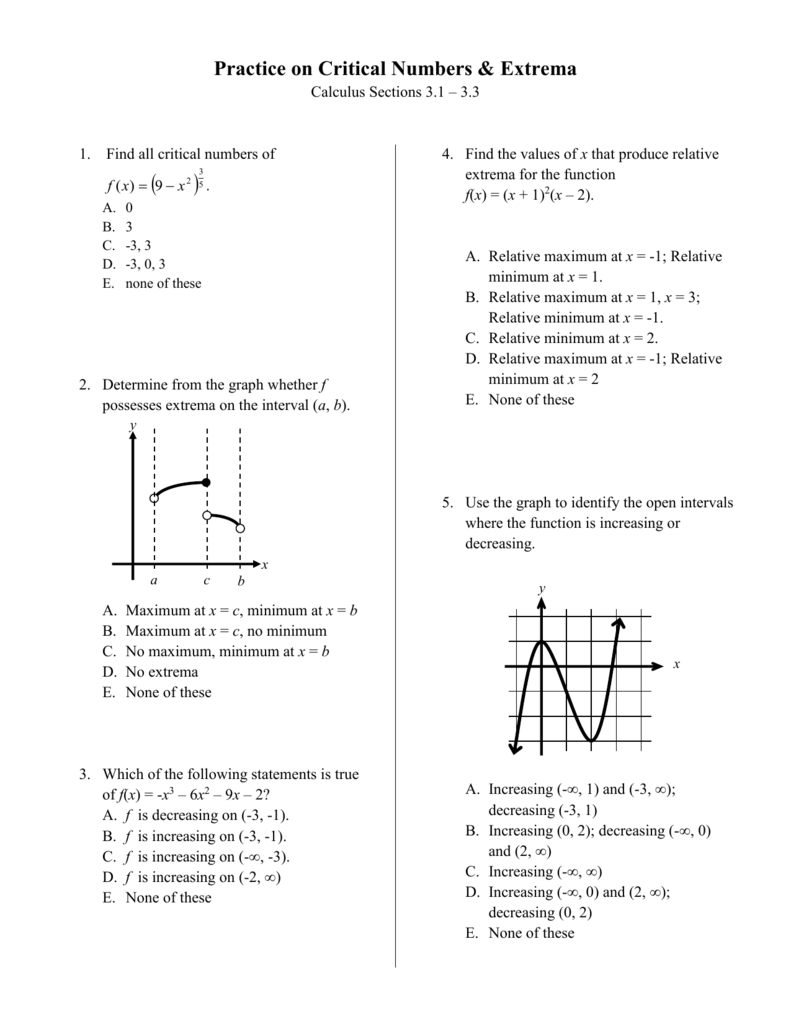



Practice On Critical Numbers Extrema
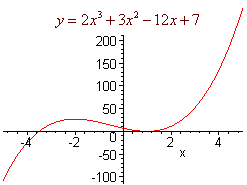



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



5 3 A Curve Sketching Ppt Video Online Download
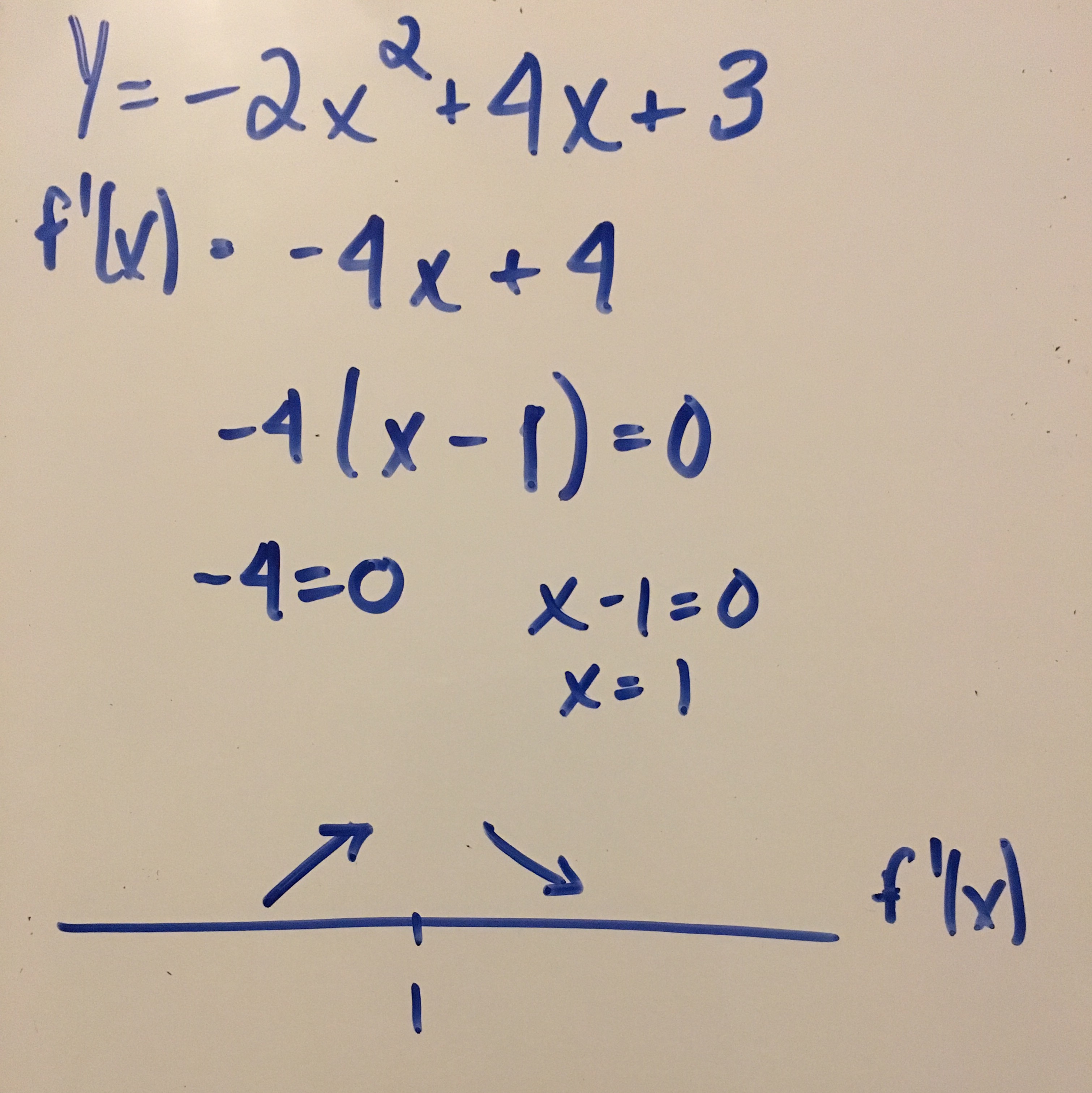



How Do You Find The Intervals Of Increasing And Decreasing Using The First Derivative Given Y 2x 2 4x 3 Socratic




X 1x Is Increasing On 1
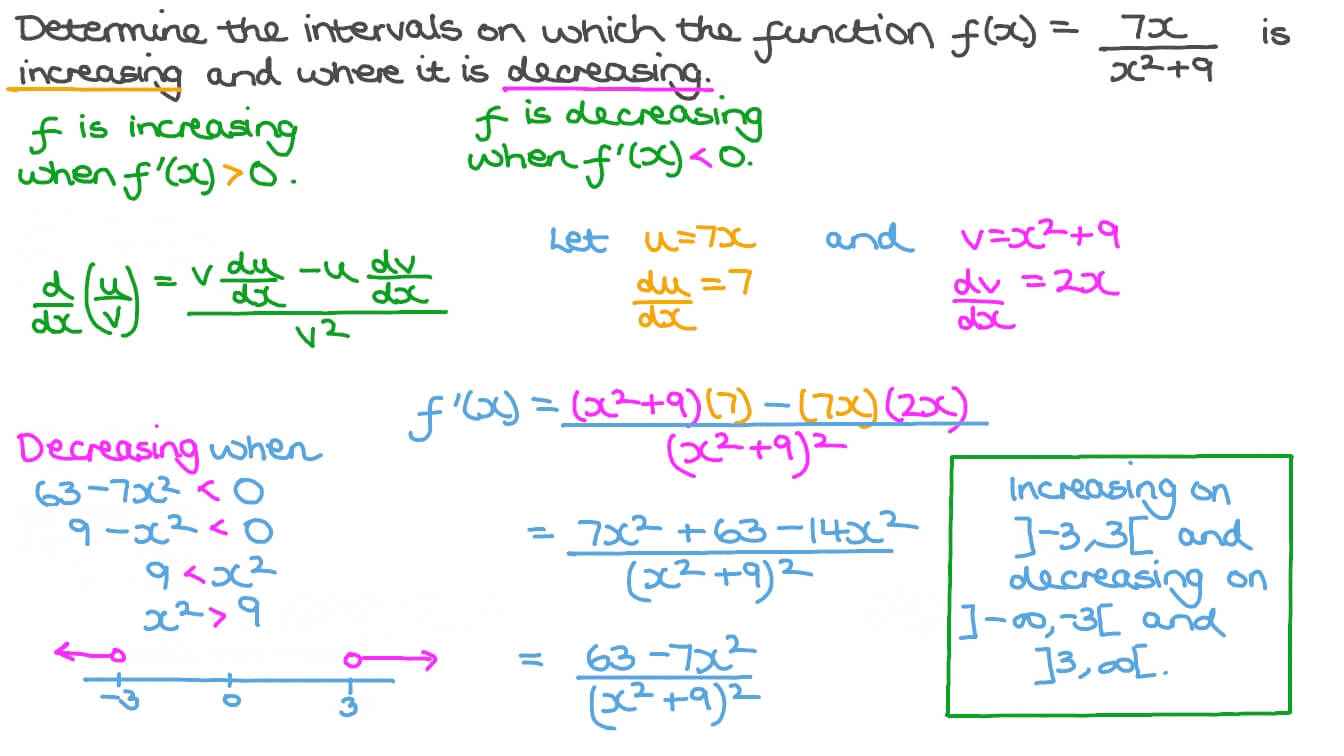



Question Video Finding The Intervals Of Increasing And Decreasing Of A Rational Function Nagwa
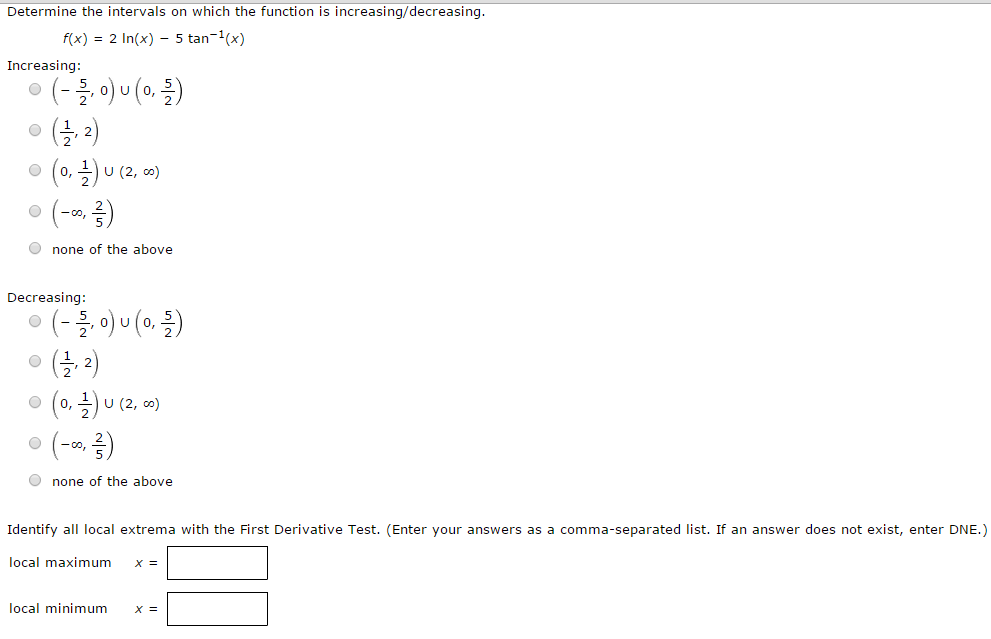



Determine The Intervals On Which The Function Is Chegg Com



Increasing And Decreasing Functions



Increasing And Decreasing Functions Find The Chegg Com




Find The Intervals In Which The Function F X Log 1 X Frac 2 X 2 X Is Strictly Increasing Or Decreasing




Find The Intervals In Which The Function F Given By F X X 3 1 X 3 X 0 Is Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Misc 7 Find Intervals F X X3 1 X3 X 0 Is Increasing
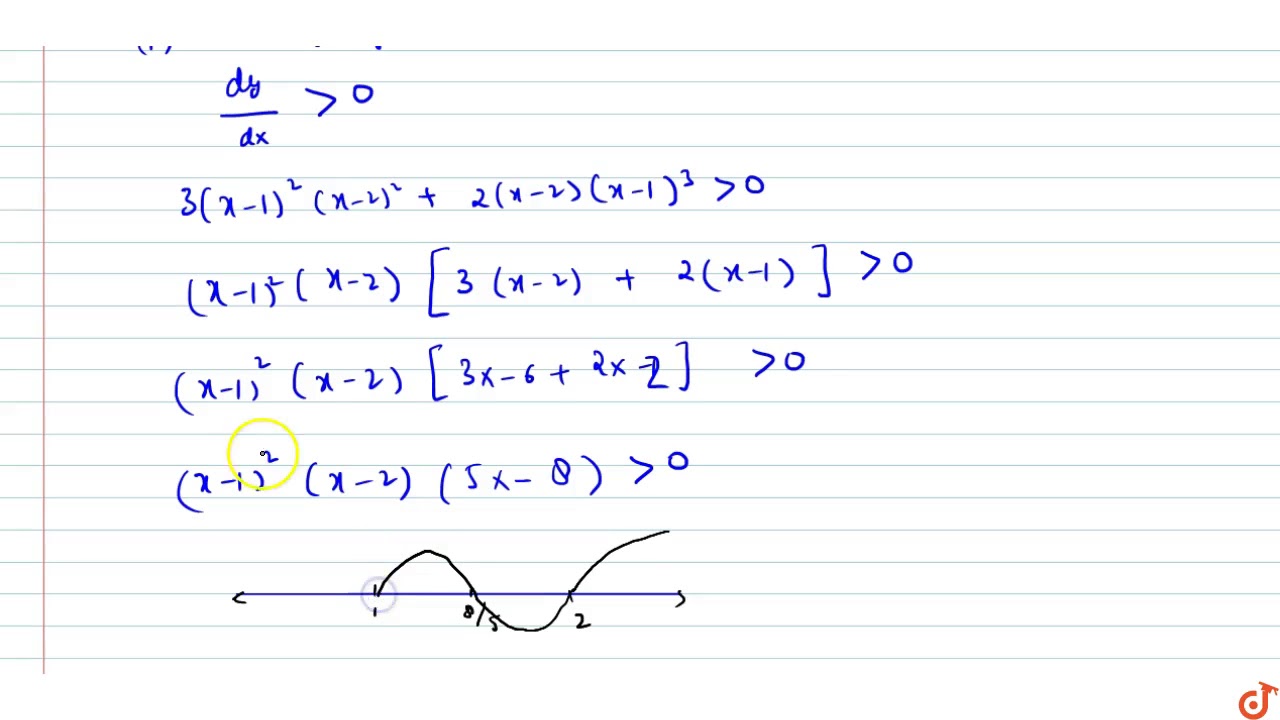



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 3 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube



Pslv Soln Rational Functions
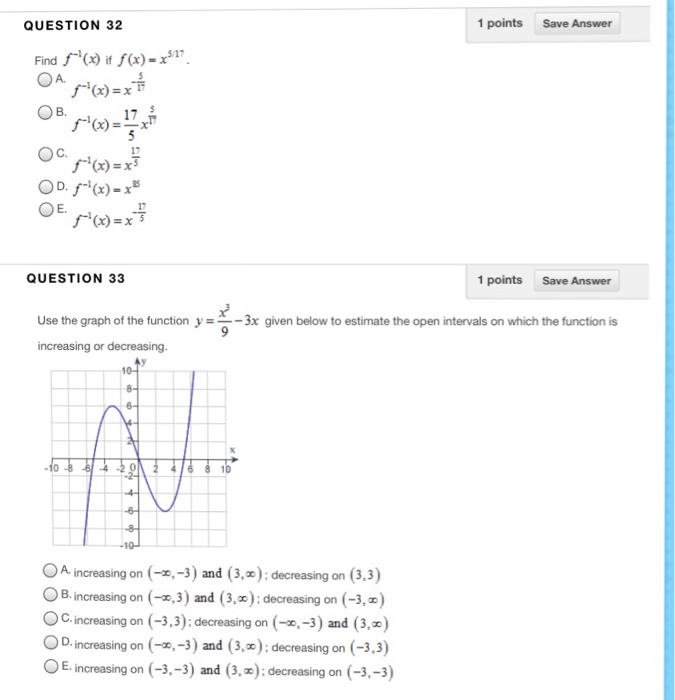



Find F 1 X If F X X 5 17 A F 1 X X Chegg Com




For Which Values Of X The Function F X X X 2 1 Is Increasing And For Which Values Of X It Is Decreasing



Describing The Graph Of A Function




Increasing Decreasing Functions A Function F Is Increasing On An Interval If For Any X 1 And X 2 In The Interval X 1 X 2 Implies F X 1 F X Ppt Download




Show That F X 1 1 X 2 Is Neither Increasing Nor Decreasing On R
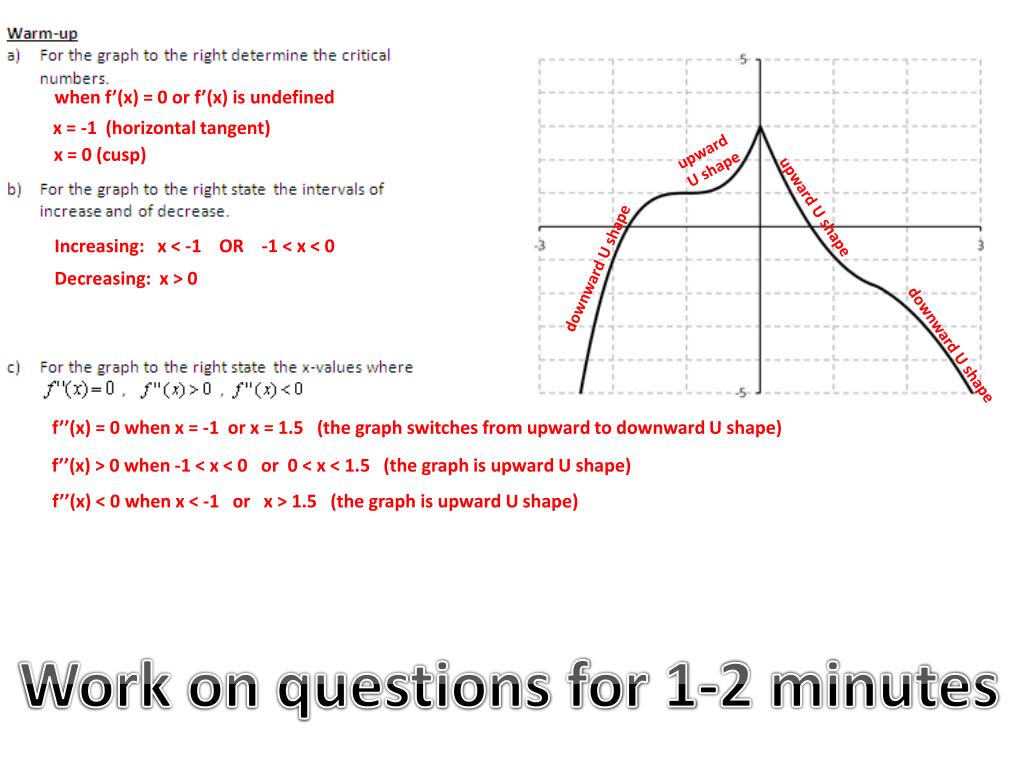



Ppt When F X 0 Or F X Is Undefined Powerpoint Presentation Id




Ex 6 2 11 Prove F X X2 X 1 Is Neither Strictly Increasing
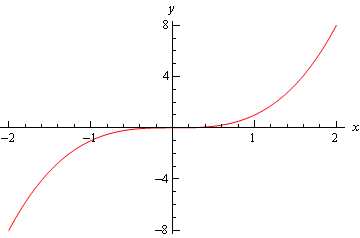



Calculus I The Shape Of A Graph Part Ii



Determine The Intervals On Which Each Function F Is Increasing Or Decreasing Mathskey Com



Answered The Function F X X 1 X Is 2p O Bartleby



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿